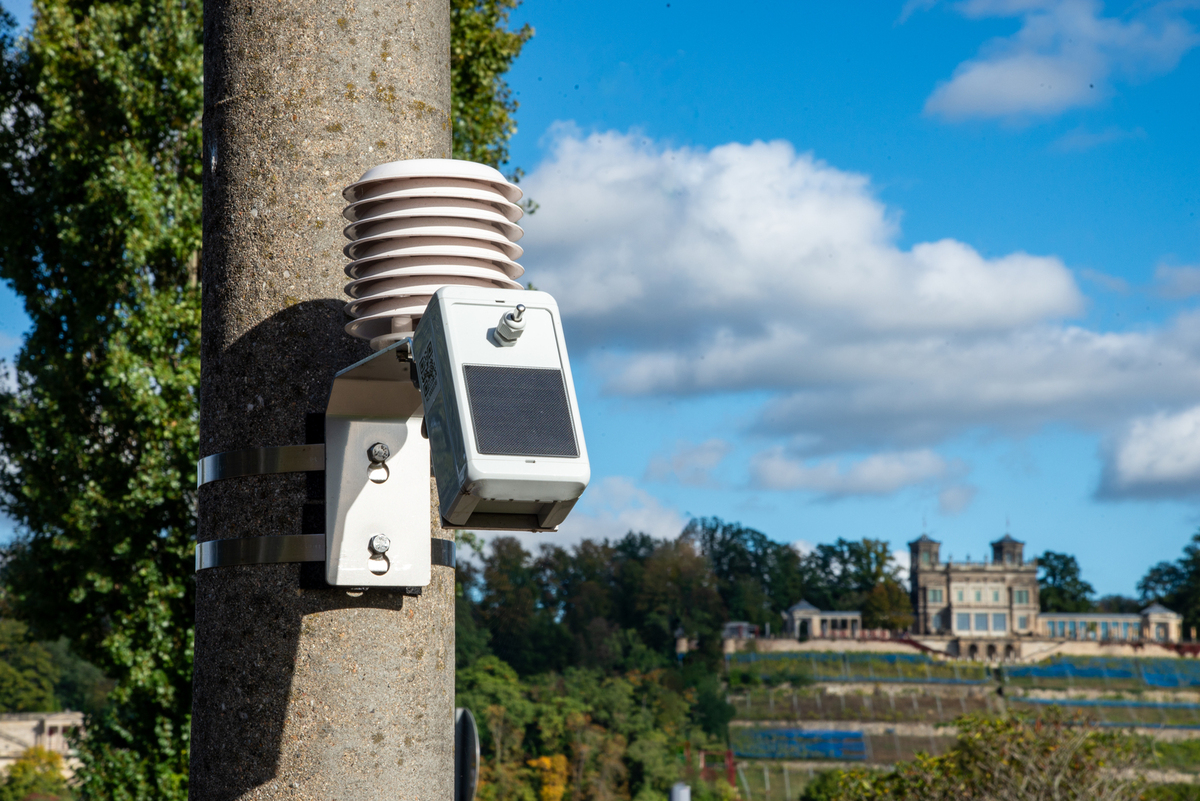
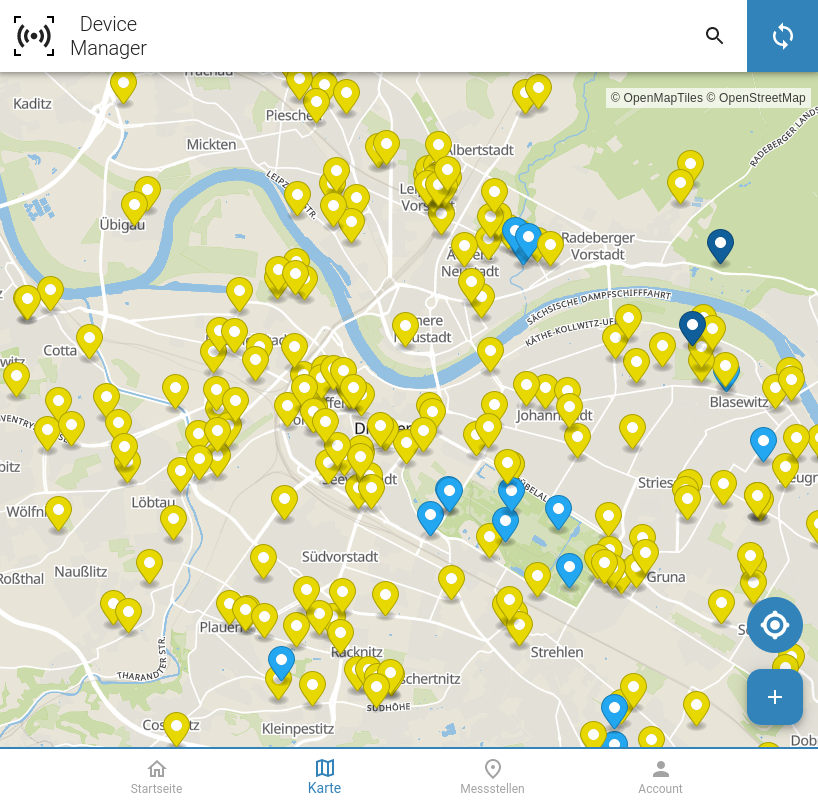
Smart sensor network in Dresden: tracking urban heat islands
A measurement network with almost 300 sensor nodes is operated in Dresden. With this large number of devices, the city can be well covered. The selection of the locations followed urban planning and urban climate criteria, since the project is intended to measure heat island effects as well as to monitor local climate changes, e.g. as a result of construction measures.
For evaluation purposes, the sensor measurement data will be blended with numerous other geo-information. In particular, the collected data is fed into an artificial neural network that learns relationships between temperature behavior and the hyperlocal urban structure.
Direct, eco-friendly installation of sensors in urban areas
The trained model is used to interpolate the measured data into the surface and will enable simulations for urban planning issues and climate change adaptation measures in the future. The roll-out of the sensor nodes and subsequent maintenance operations are mainly carried out by cargo bike. This is climate-friendly, very efficient and time-saving, especially in urban areas, since installation sites in pedestrian zones and parks can be approached directly.